@[toc]
# 1. Vuex概述
# 1.1 组件间共享数据的方式
之前学习过的一些方法 【Vue】组件定义与使用-组件间通信 (opens new window) 【Vue】vuex - 状态自管理应用 - state - view - actions (opens new window)
父向子传值:v-bind 属性绑定
子向父传值:v-on 事件绑定
兄弟组件之间共享数据: EventBus
$on接收数据的那个组件$emit发送数据的那个组件
# 1.2 Vuex 是什么(实现组件间数据共享)
Vuex 是实现组件全局状态(数据)管理的一种机制,可以方便的实现组件之间数据的共享.
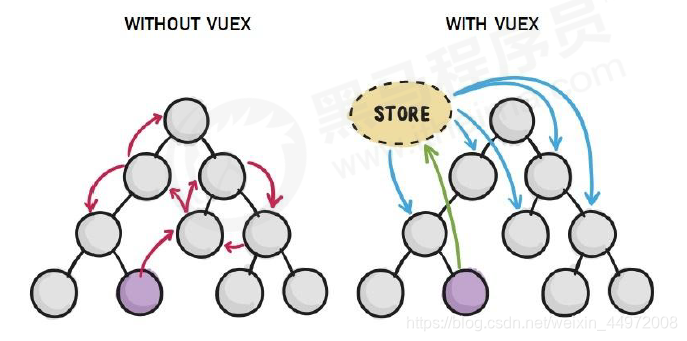
# 1.3 使用 Vuex 统一管理状态的好处
① 能够在 vuex 中集中管理共享的数据,易于开发和后期维护 ② 能够高效地实现组件之间的数据共享,提高开发效率 ③ 存储在 vuex 中的数据都是响应式的,能够实时保持数据与页面的同步
# 1.4 什么样的数据适合存储到 Vuex 中
一般情况下,只有组件之间共享的数据,才有必要存储到 vuex 中; 对于组件中的私有数据,依旧存储在组件自身的 data 中即可。
# 2. Vuex 的基本使用
# 1. 安装 vuex 依赖包
cnpm install vuex --save
# 2. 导入 vuex 包
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
# 3. 创建 store 对象
const store = new Vuex.Store({
// state 中存放的就是全局共享的数据
state: { count: 0 }
})
# 4. 将 store 对象挂载到 vue 实例中
new Vue({
el: '#app',
render: h => h(app),
router,
// 将创建的共享数据对象,挂载到 Vue 实例中
// 所有的组件,就可以直接从 store 中获取全局的数据了
store
})
# 3. 案例项目1 计数器
推荐自动生成---在vue ui 面板中创建一个vue项目,添加vuex
# Addition.vue
<template>
<div>
<h3>当前最新的count值为:xxx</h3>
<button>+1</button>
</div>
</template>
# Subtraction.vue
<template>
<div>
<h3>当前最新的count值为:xxx</h3>
<button>-1</button>
</div>
</template>
# App.vue
<template>
<div>
<my-addition></my-addition>
<p>------------</p>
<my-subtraction></my-subtraction>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Addition from './components/Addition.vue'
import Subtraction from './components/Subtraction.vue'
export default {
data() {
return {}
},
components: {
'my-addition': Addition,
'my-subtraction': Subtraction
}
}
</script>
最后在项目根目录(与src平级)中创建 .prettierrc 文件,编写代码如下
{
"semi":false,
"singleQuote":true
}
# 4. Vuex 的核心概念
# 4.1 核心概念概述
Vuex 中的主要核心概念如下:
- State
- Mutation
- Action
- Getter
# 4.2 State (声明)
- State 提供唯一的公共数据源,所有共享的数据都要统一放到 Store 的 State 中进行存储
例如,打开项目中的store/index.js文件,在State对象中可以添加我们要共享的数据,如:count:0
// 创建store数据源,提供唯一公共数据
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
}
})
# 案例 store/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
}
})
# 组件访问 State 中数据的第一种方式
this.$store.state.全局数据名称
# 案例 Addition.vue
<template>
<div>
<h3>当前最新的count值为:{{ $store.state.count }}</h3>
<button>+1</button>
</div>
</template>
# 组件访问 State 中数据的第二种方式
// 1. 从 vuex 中按需导入 mapState 函数
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
通过刚才导入的 mapState 函数,将当前组件需要的全局数据,映射为当前组件的
computed 计算属性:
// 2. 将全局数据,映射为当前组件的计算属性
computed: {
...mapState(['count'])
}
# 案例 Subtraction.vue
<template>
<div>
<h3>当前最新的count值为:{{ count }}</h3>
<button>-1</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
export default {
data() {
return {}
},
computed: {
...mapState(['count'])
}
}
</script>
# 4.3 Mutation (变化)
Mutation 用于变更 Store中的数据。 ①只能通过 mutation 变更 Store 数据,不可以直接操作 Store 中的数据。 ②通过这种方式虽然操作起来稍微繁琐一些,但是可以集中监控所有数据的变化
# 4.3.1 触发的第一种方式
// 定义 Mutation
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: { count: 0 },
mutations: {
add(state) {
// 变更状态
state.count++
}
}
})
// 触发mutation
methods: {
handle1() { // 触发 mutations 的第一种方式
this.$store.commit('add')
}
}
可以在触发 mutations 时传递参数:
// 定义Mutation
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
mutations: {
addN(state, step) {
// 变更状态
state.count += step
}
}
})
// 触发mutation
methods: {
handle2() {
// 在调用 commit 函数,
// 触发 mutations 时携带参数
this.$store.commit('addN', 3)
}
}
# 案例 store/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
mutations: {
add(state) {
// 变更状态
state.count++
},
addN(state, step) {
// 变更状态
state.count += step
}
}
})
# 案例 Addition.vue
<template>
<div>
<h3>当前最新的count值为:{{ $store.state.count }}</h3>
<button @click="btnHandler1">+1</button>
<button @click="btnHandler2">+N</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {}
},
methods: {
btnHandler1() {
this.$store.commit('add')
},
btnHandler2() {
// commit作用就是调用某个mutation函数
this.$store.commit('addN', 3)
}
}
}
</script>
# 4.3.1 触发的第二种方式
this.$store.commit() 是触发 mutations 的第一种方式,触发 mutations 的第二种方式:
// 1. 从 vuex 中按需导入 mapMutations 函数
import { mapMutations } from 'vuex'
通过刚才导入的 mapMutations 函数,将需要的 mutations 函数,映射为当前组件的 methods 方法:
// 2. 将指定的 mutations 函数,映射为当前组件的 methods 函数
methods: {
...mapMutations(['add', 'addN'])
}
# 案例 store/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
mutations: {
add(state) {
// 变更状态
state.count++
},
addN(state, step) {
// 变更状态
state.count += step
},
sub(state) {
state.count--
},
subN(state, step) {
// 变更状态
state.count -= step
}
}
})
# 案例 Subtraction.vue
<template>
<div>
<h3>当前最新的count值为:{{ count }}</h3>
<button @click="btnHandler1">-1</button>
<button @click="btnHandler2">-N</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapState, mapMutations } from 'vuex'
export default {
data() {
return {}
},
computed: {
...mapState(['count'])
},
methods: {
...mapMutations(['sub', 'subN']),
btnHandler1() {
this.sub()
},
btnHandler2() {
this.subN(3)
}
}
}
</script>
# 4.4 Action (行动)
Action 用于处理异步任务。
如果通过异步操作变更数据,必须通过 Action,而不能使用 Mutation,但是在 Action 中还是要通过触发Mutation 的方式间接变更数据。
# 触发的第一种方式
// 定义 Action
const store = new Vuex.Store({
// ...省略其他代码
mutations: {
add(state) {
state.count++
}
},
actions: {
addAsync(context) {
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('add')
}, 1000)
}
}
})
// 触发 Action
methods: {
handle() {
// 触发 actions 的第一种方式
this.$store.dispatch('addAsync')
}
}
触发 actions 异步任务时携带参数:
// 定义 Action
const store = new Vuex.Store({
// ...省略其他代码
mutations: {
addN(state, step) {
state.count += step
}
},
actions: {
addNAsync(context, step) {
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('addN', step)
}, 1000)
}
}
})
// 触发 Action
methods: {
handle() {
// 在调用 dispatch 函数,
// 触发 actions 时携带参数
this.$store.dispatch('addNAsync', 5)
}
}
# 案例 store/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
// 只有 mutations 中定义的函数,才有权利修改 state 中的数据
mutations: {
add(state) {
// 变更状态
state.count++
},
addN(state, step) {
// 变更状态
state.count += step
},
sub(state) {
state.count--
},
subN(state, step) {
// 变更状态
state.count -= step
}
},
actions: {
addAsync(context) {
setTimeout(() => {
// 在actions中不能直接修改state中的数据
// 必须通过 context.commit() 触发某个 mutations 才行
context.commit('add')
}, 1000)
},
addNAsync(context, step) {
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('addN', step)
}, 1000)
}
}
})
# 案例 Addition.vue
<template>
<div>
<h3>当前最新的count值为:{{ $store.state.count }}</h3>
<button @click="btnHandler1">+1</button>
<button @click="btnHandler2">+N</button>
<button @click="btnHandler3">+1 Async</button>
<button @click="btnHandler4">+N Async</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {}
},
methods: {
btnHandler1() {
this.$store.commit('add')
},
btnHandler2() {
// commit作用就是调用某个mutation函数
this.$store.commit('addN', 3)
},
// 异步让count自增+1
btnHandler3() {
// 这里的 dispatch 函数 专门用来触发 action
this.$store.dispatch('addAsync')
},
btnHandler4() {
this.$store.dispatch('addNAsync', 5)
}
}
}
</script>
# 触发的第二种方式
this.$store.dispatch() 是触发 actions 的第一种方式,触发 actions 的第二种方式:
// 1. 从 vuex 中按需导入 mapActions 函数
import { mapActions } from 'vuex'
通过刚才导入的 mapActions 函数,将需要的 actions 函数,映射为当前组件的 methods 方法:
// 2. 将指定的 actions 函数,映射为当前组件的 methods 函数
methods: { ...mapActions(['addASync', 'addNASync']) }
# 案例 store/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
// 只有 mutations 中定义的函数,才有权利修改 state 中的数据
mutations: {
add(state) {
// 变更状态
state.count++
},
addN(state, step) {
// 变更状态
state.count += step
},
sub(state) {
state.count--
},
subN(state, step) {
// 变更状态
state.count -= step
}
},
actions: {
addAsync(context) {
setTimeout(() => {
// 在actions中不能直接修改state中的数据
// 必须通过 context.commit() 触发某个 mutations 才行
context.commit('add')
}, 1000)
},
addNAsync(context, step) {
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('addN', step)
}, 1000)
},
subAsync(context) {
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('sub')
}, 1000)
},
subNAsync(context, step) {
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('subN', step)
}, 1000)
}
}
})
# 案例 Subtraction.vue
<template>
<div>
<h3>当前最新的count值为:{{ count }}</h3>
<button @click="btnHandler1">-1</button>
<button @click="btnHandler2">-N</button>
<button @click="btnHandler3">-1 Async</button>
<button @click="btnHandler4">-N Async</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapState, mapMutations, mapActions } from 'vuex'
export default {
data() {
return {}
},
computed: {
...mapState(['count'])
},
methods: {
...mapMutations(['sub', 'subN']),
...mapActions(['subAsync', 'subNAsync']),
btnHandler1() {
this.sub()
},
btnHandler2() {
this.subN(3)
},
btnHandler3() {
this.subAsync()
},
btnHandler4() {
this.subNAsync(5)
}
}
}
</script>
# 案例 简化 Subtraction.vue
<template>
<div>
<h3>当前最新的count值为:{{ count }}</h3>
<button @click="sub">-1</button>
<button @click="subN(3)">-N</button>
<button @click="subAsync">-1 Async</button>
<button @click="subNAsync(5)">-N Async</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapState, mapMutations, mapActions } from 'vuex'
export default {
data() {
return {}
},
computed: {
...mapState(['count'])
},
methods: {
...mapMutations(['sub', 'subN']),
...mapActions(['subAsync', 'subNAsync'])
}
}
</script>
# 4.5 Getter
Getter 用于对 Store 中的数据进行加工处理形成新的数据。只起到包装的作用。 ①Getter 可以对 Store 中已有的数据加工处理之后形成新的数据,类似 Vue 的计算属性。 ②Store 中数据发生变化,Getter 的数据也会跟着变化。
它只会包装Store中保存的数据,并不会修改Store中保存的数据,当Store中的数据发生变化时,Getter生成的内容也会随之变化
// 定义 Getter
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
getters: {
showNum: state => {
return '当前最新的数量是【'+ state.count +'】'
}
}
})
# 使用 getters 的第一种方式
this.$store.getters.名称
# 案例 store/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
// 只有 mutations 中定义的函数,才有权利修改 state 中的数据
mutations: {
add(state) {
// 变更状态
state.count++
},
addN(state, step) {
// 变更状态
state.count += step
},
sub(state) {
state.count--
},
subN(state, step) {
// 变更状态
state.count -= step
}
},
actions: {
addAsync(context) {
setTimeout(() => {
// 在actions中不能直接修改state中的数据
// 必须通过 context.commit() 触发某个 mutations 才行
context.commit('add')
}, 1000)
},
addNAsync(context, step) {
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('addN', step)
}, 1000)
},
subAsync(context) {
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('sub')
}, 1000)
},
subNAsync(context, step) {
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('subN', step)
}, 1000)
}
},
getters: {
showNum(state) {
return `当前最新的数量是【${state.count}】`
}
}
})
# 案例 Addition.vue
<template>
<div>
<!-- <h3>当前最新的count值为:{{ $store.state.count }}</h3> -->
<h3>{{ $store.getters.showNum }}</h3>
<button @click="btnHandler1">+1</button>
<button @click="btnHandler2">+N</button>
<button @click="btnHandler3">+1 Async</button>
<button @click="btnHandler4">+N Async</button>
</div>
</template>
# 使用 getters 的第二种方式
import { mapGetters } from 'vuex'
computed: {
...mapGetters(['showNum'])
}
# 案例 Subtraction.vue
<template>
<div>
<!-- <h3>当前最新的count值为:{{ count }}</h3> -->
<h3>{{ showNum }}</h3>
<button @click="sub">-1</button>
<button @click="subN(3)">-N</button>
<button @click="subAsync">-1 Async</button>
<button @click="subNAsync(5)">-N Async</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapState, mapMutations, mapActions, mapGetters } from 'vuex'
export default {
data() {
return {}
},
computed: {
...mapState(['count']),
...mapGetters(['showNum'])
},
methods: {
...mapMutations(['sub', 'subN']),
...mapActions(['subAsync', 'subNAsync'])
}
}
</script>
# 4.6 展示

# 5. 案例项目2 TodoList
# 5.1 初始化项目
① 通过 vue ui 命令打开可视化面板,创建新项目 vuex_todolist
② 安装运行依赖 axios 和 ant-design-vue
③ 实现 Todos 基本布局(基于已有样式模板)
# main.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
// 1. 导入 ant-design-vue 组件库
import Antd from 'ant-design-vue'
// 2. 导入组件库的样式表
import 'ant-design-vue/dist/antd.css'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
// 3. 安装组件库
Vue.use(Antd)
new Vue({
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount('#app')
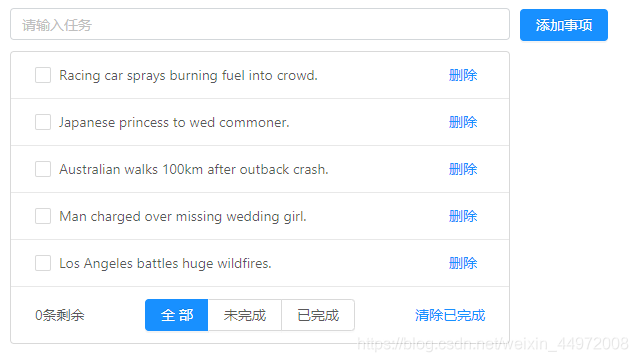
# App.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<a-input placeholder="请输入任务" class="my_ipt" />
<a-button type="primary">添加事项</a-button>
<a-list bordered :dataSource="list" class="dt_list">
<a-list-item slot="renderItem" slot-scope="item">
<!-- 复选框 -->
<a-checkbox>{{ item.info }}</a-checkbox>
<!-- 删除链接 -->
<a slot="actions">删除</a>
</a-list-item>
<!-- footer区域 -->
<div slot="footer" class="footer">
<!-- 未完成的任务个数 -->
<span>0条剩余</span>
<!-- 操作按钮 -->
<a-button-group>
<a-button type="primary">全部</a-button>
<a-button>未完成</a-button>
<a-button>已完成</a-button>
</a-button-group>
<!-- 把已经完成的任务清空 -->
<a>清除已完成</a>
</div>
</a-list>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'app',
data() {
return {
list: [
{
id: 0,
info: 'Racing car sprays burning fuel into crowd.',
done: false
},
{ id: 1, info: 'Japanese princess to wed commoner.', done: false },
{
id: 2,
info: 'Australian walks 100km after outback crash.',
done: false
},
{ id: 3, info: 'Man charged over missing wedding girl.', done: false },
{ id: 4, info: 'Los Angeles battles huge wildfires.', done: false }
]
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
#app {
padding: 10px;
}
.my_ipt {
width: 500px;
margin-right: 10px;
}
.dt_list {
width: 500px;
margin-top: 10px;
}
.footer {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
align-items: center;
}
</style>
# 5.2 完成具体功能
# 5.2.1 动态加载任务列表list数据
# 1. main.js 导入并挂载store
import store from './store/index.js'
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
store
}).$mount('#app')
# 2. 将App.vue中data的list数组 剪切 到public/list.json中
[
{
"id": 0,
"info": "Racing car sprays burning fuel into crowd.",
"done": false
},
{ "id": 1, "info": "Japanese princess to wed commoner.", "done": false },
{
"id": 2,
"info": "Australian walks 100km after outback crash.",
"done": false
},
{ "id": 3, "info": "Man charged over missing wedding girl.", "done": false },
{ "id": 4, "info": "Los Angeles battles huge wildfires.", "done": false }
]
# 3. 在store/index.js中使用axios发请求获取数据
# 4. 将数据存储到state中,在mutations中为list赋值
App.vue
<script>
export default {
name: 'app',
data() {
return {
list: []
}
},
created() {
this.$store.dispatch('getList')
}
}
</script>
store/index.js
import axios from 'axios'
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
// 所有的任务列表
list: []
},
mutations: {
initList(state, list) {
state.list = list
}
},
actions: {
getList(context) {
axios.get('./list.json').then(({ data }) => {
console.log(data) // (5)[{…}, {…}, {…}, {…}, {…}]
context.commit('initList', data)
})
}
},
modules: {}
})
# 5. 在App.vue中将store中的数据映射过来
<script>
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'app',
data() {
return {}
},
created() {
this.$store.dispatch('getList')
},
computed: {
...mapState(['list'])
}
}
</script>
# 5.2.2 文本框内容 与 store数据 双向绑定
# 1. 创建state声明 inputValue
store/index.js
state: {
// 所有的任务列表
list: [],
// 文本框的内容
inputValue: 'aaa'
}
# 2. 将全局inputVale映射到当前组件的计算属性中---组件中调用state(方式二)
App.vue
<template>
<a-input placeholder="请输入任务" :value="inputValue"/>
</template>
<script>
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
export default {
computed: {
...mapState(['list', 'inputValue'])
</script>
# 3. 监听文本框内容变化 change事件(获取输入框的值)
App.vue
<template>
<a-input placeholder="请输入任务" @change="handleInputChange"/>
</template>
<script>
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
export default {
computed: {
...mapState(['list', 'inputValue'])
},
methods: {
// 监听文本框内容变化
handleInputChange(e) {
console.log(e.target.value)
}
}
}
</script>
# 4. 将输入框获得的值 保存到 inputVaule上 (为state赋值)
store/index.js
mutations: {
setInputValue(state, val) {
state.inputValue = val
}
}
# 5. 组件中调用mutations(方式一)
App.vue/script/methods
// 监听文本框内容变化
handleInputChange(e) {
// console.log(e.target.value)
this.$store.commit('setInputValue', e.target.value)
}
# 5.2.3 添加任务事项
# 1. 为button按钮绑定单击事件处理函数
App.vue
<a-button type="primary" @click="addItemTodoList">添加事项</a-button>
# 2. 判断输入是否为空,为空就返回错误信息
App.vue/script/methods
methods: {
// 向列表中新增 item 项
addItemTodoList() {
if (this.inputValue.trim().length <= 0) {
return this.$message.warning('文本框内容不能为空!')
}
}
}
# 3. mutations中定义 添加 列表项 (改变list)
store/index.js
state: {
// 下一个id
nextId: 5
},
mutations: {
// 添加列表项
addItem(state) {
const obj = {
id: state.nextId,
info: state.inputValue.trim(),
done: false
}
state.list.push(obj)
state.nextId++
state.inputValue = ''
}
}
# 4. 输入内容不为空 就 调用mutations中的addItem执行添加任务项
App.vue/script/methods
// 向列表中新增 item 项
addItemTodoList() {
if (this.inputValue.trim().length <= 0) {
return this.$message.warning('文本框内容不能为空!')
}
this.$store.commit('addItem')
}
# 5.2.4 删除任务事项
# App.vue/template
<a slot="actions" @click="removeItemById(item.id)">删除</a>
# store/index.js/mutations
mutations: {
// 删除id对应的列表项
removeItem(state, id) {
// 1. 根据id查找对应项的索引
const index = state.list.findIndex(x => x.id === id)
if (index !== -1) {
// 2. 根据索引删除对应元素
state.list.splice(index, 1)
}
}
}
# App.vue/script/methods
methods: {
// 根据id删除对应任务事项
removeItemById(id) {
this.$store.commit('removeItem', id)
}
}
# 5.2.5 动态绑定复选框的选中状态
App.vue
<!-- 复选框 -->
<a-checkbox :checked="item.done">{{ item.info }}</a-checkbox>
# 5.2.6 修改任务事项的完成状态
# App.vue/template
<!-- 复选框 -->
<a-checkbox :checked="item.done" @change="(e) => {cbStatusChanged(e, item.id)}">{{ item.info }}</a-checkbox>
# App.vue/script/mehods
// 监听复选框选中状态变化的事件
cbStatusChanged(e, id) {
// 通过 e.target.checked 可以接收到最新的选中状态
const params = {
id: id,
status: e.target.checked
}
this.$store.commit('changeStatus', params)
}
# store/index.js/mutations
// 修改列表项中的选中状态
changeStatus(state, param) {
const index = state.list.findIndex(x => x.id === param.id)
if (index !== -1) {
state.list[index].done = param.status
}
}
# 5.2.7 统计未完成的任务的条数
# store/index.js/getters
getters: {
// 统计未完成任务条数
unDoneLength(state) {
return state.list.filter(x => x.done === false).length
}
}
# App.vue/script
import { mapState, mapGetters } from 'vuex'
export default {
computed: {
...mapState(['list', 'inputValue']),
...mapGetters(['unDoneLength'])
}
}
# App.vue/template
<!-- 未完成的任务个数 -->
<span>{{ unDoneLength }}条剩余</span>
# 5.2.8 清除已完成的任务事项
# App.vue/template
<!-- 把已经完成的任务清空 -->
<a @click="clean">清除已完成</a>
# App.vue/script/methods
// 清除已完成的任务
clean() {
this.$store.commit('cleanDone')
}
# store/index.js/mutations
// 清除已完成的任务
cleanDone(state) {
state.list = state.list.filter(x => x.done === false)
}
# 5.2.9 实现任务列表点击高亮切换
# 1. 为不同按钮绑定相同的单击响应函数changeList
App.vue/template
<!-- 操作按钮 -->
<a-button-group>
<a-button type="primary" @click="changeList('all')">全部</a-button>
<a-button type="default" @click="changeList('undone')">未完成</a-button>
<a-button type="default" @click="changeList('done')">已完成</a-button>
</a-button-group>
# 2. 将接受到的字符串存储到全局的store中
store/index.js/state
viewKey: 'all'
App.vue/script/methods
// 修改页面上展示的列表数据
changeList(key){
this.$store.commit('changeViewKey', key)
}
store/index.js/mutations
// 修改视图的关键字
changeViewKey(state, key) {
state.viewKey = key
}
# 3. 将viewKey映射为当前组件的计算属性
App.vue/script/computed
...mapState(['list', 'inputValue', 'viewKey'])
# 4. 根据viewKey的值动态计算决定按钮高亮(三元表达式)
App.vue/template
<!-- 操作按钮 -->
<a-button-group>
<a-button
:type="viewKey === 'all' ? 'primary' : 'default'"
@click="changeList('all')"
>全部</a-button
>
<a-button
:type="viewKey === 'undone' ? 'primary' : 'default'"
@click="changeList('undone')"
>未完成</a-button
>
<a-button
:type="viewKey === 'done' ? 'primary' : 'default'"
@click="changeList('done')"
>已完成</a-button
>
</a-button-group>
# 5.2.10 实现任务列表数据的动态切换
# 1. 使用Getter将list进行包装,按需显示希望用户看到的数据
store/index.js/getters
// 根据viewKey的值决定list
infoList(state) {
if (state.viewKey === 'all') {
return state.list
}
if (state.viewKey === 'undone') {
return state.list.filter(x => !x.done)
}
if (state.viewKey === 'done') {
return state.list.filter(x => x.done)
}
return state.list
}
# 2. 将infoList映射到组件的计算属性中,可以删除映射的state/list
App.vue/script/computed
...mapState(['inputValue', 'viewKey']),
...mapGetters(['unDoneLength', 'infoList'])
# 3. 将infoList替代list作为动态绑定的数据源
App.vue/template
<a-list bordered :dataSource="infoList" class="dt_list">
# 5.3 效果展示
